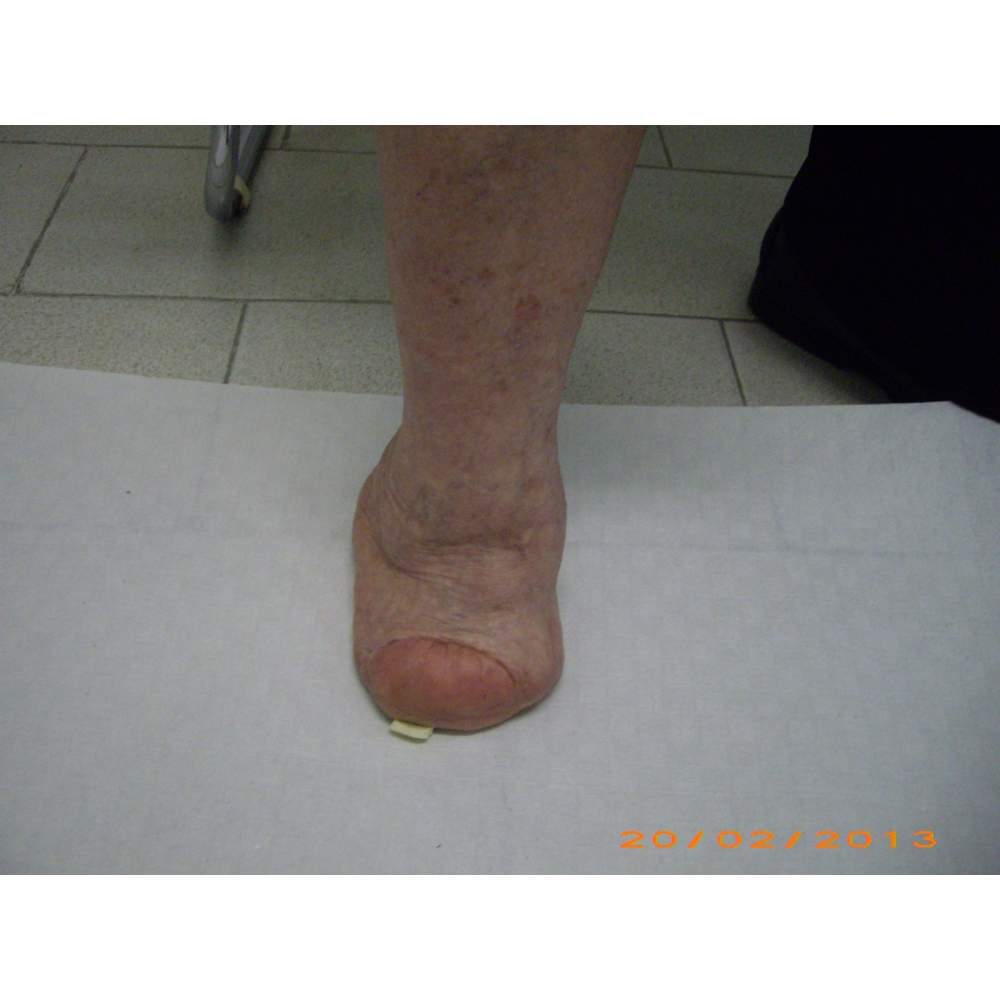
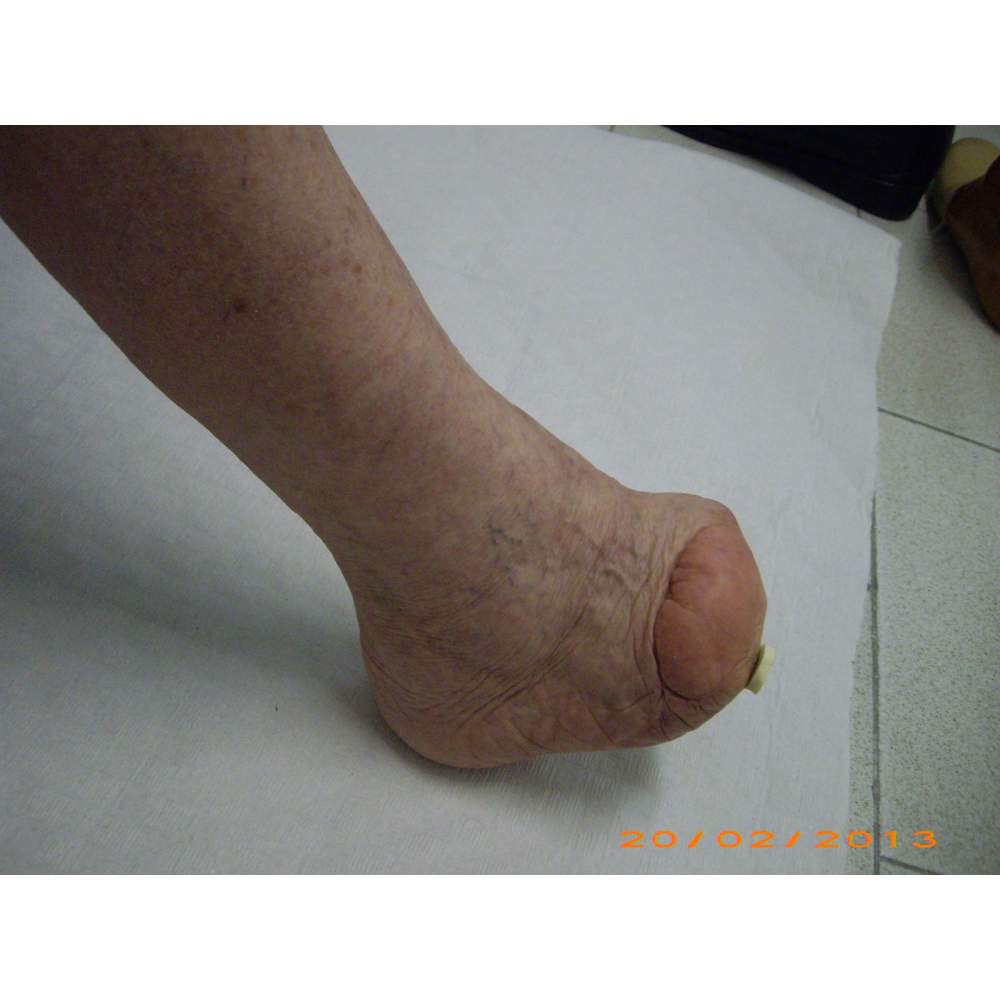
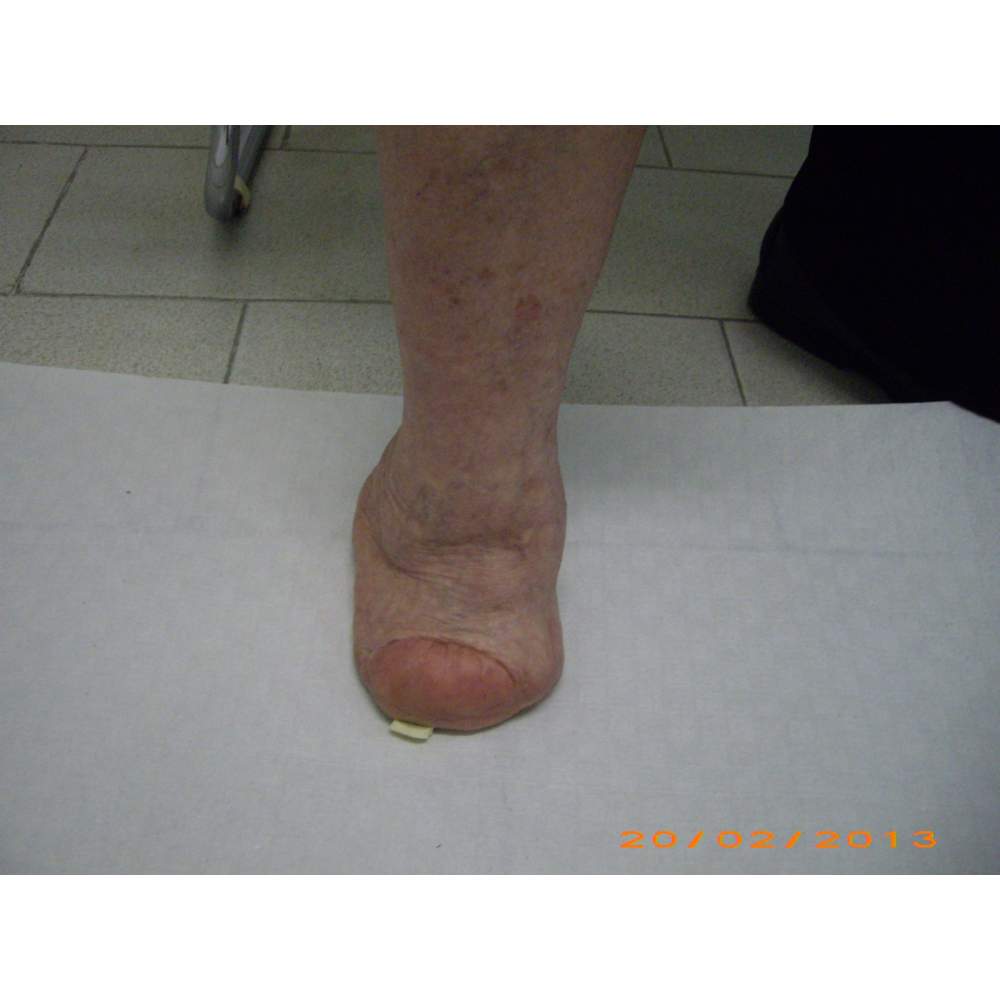
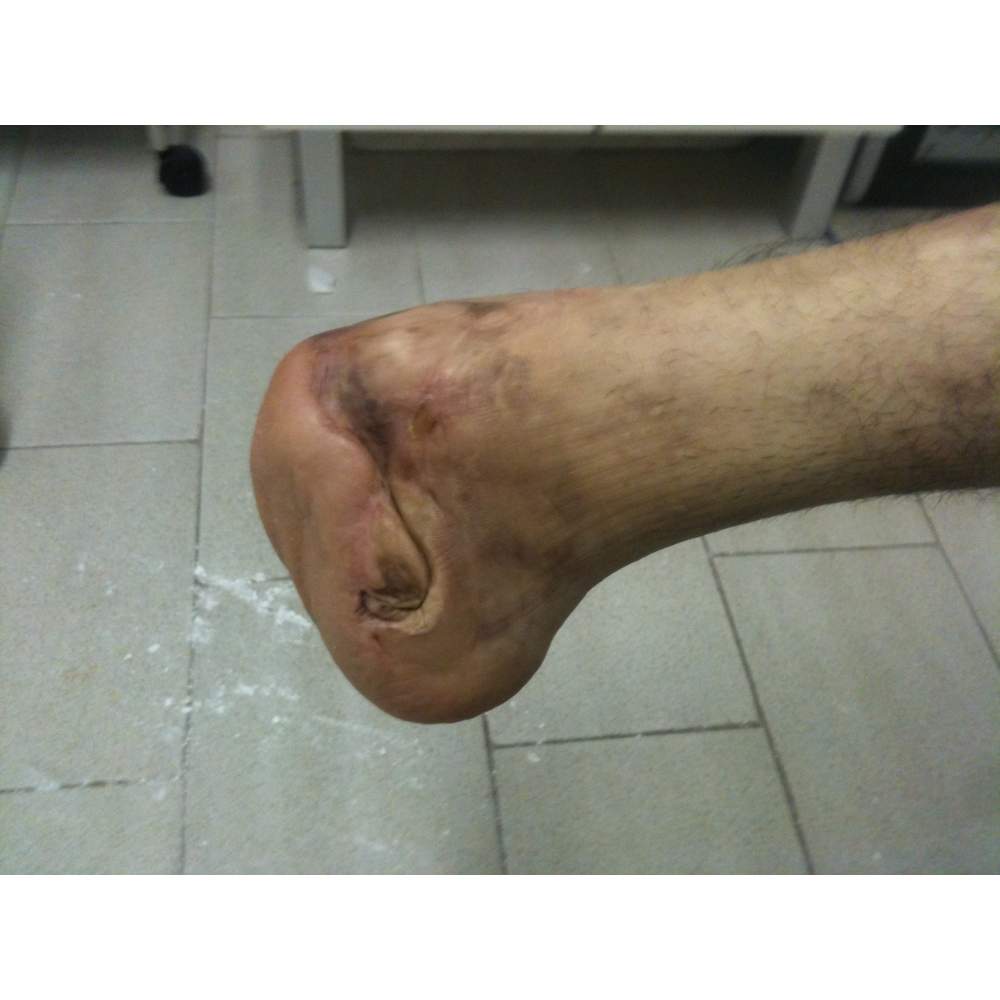
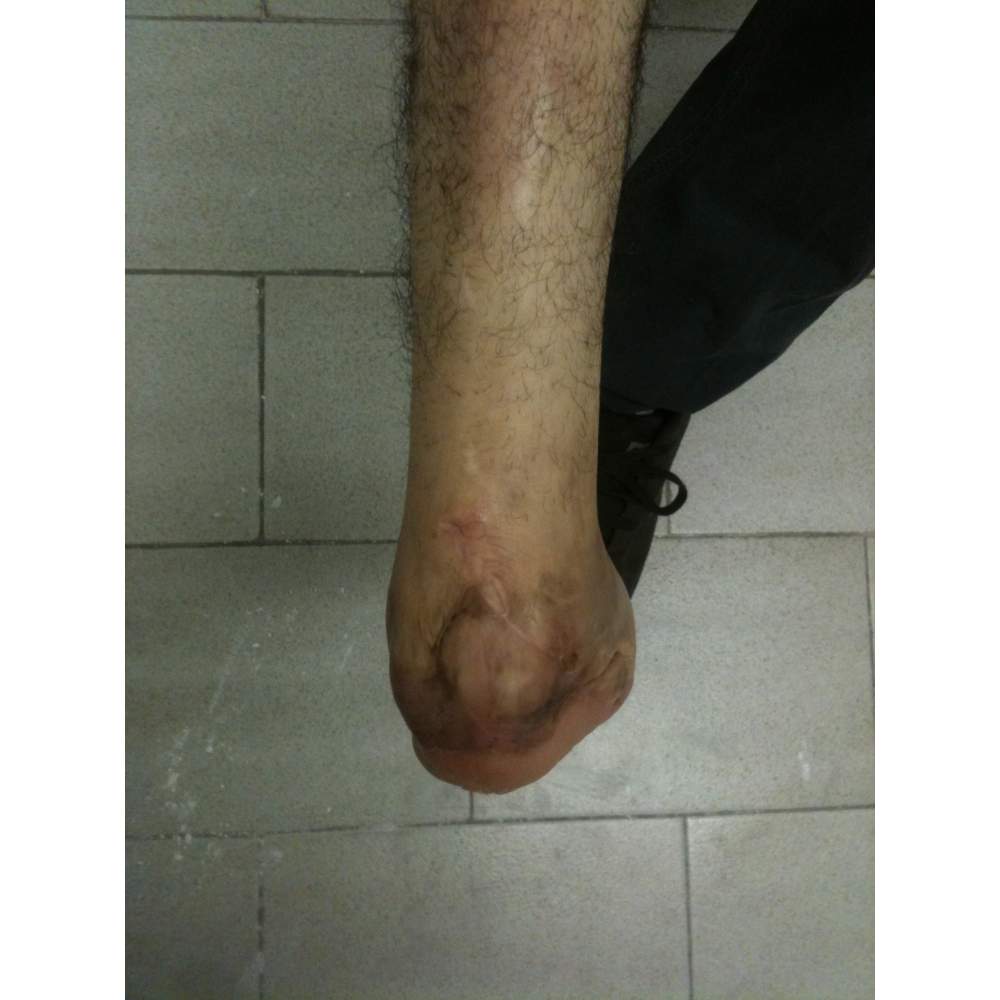
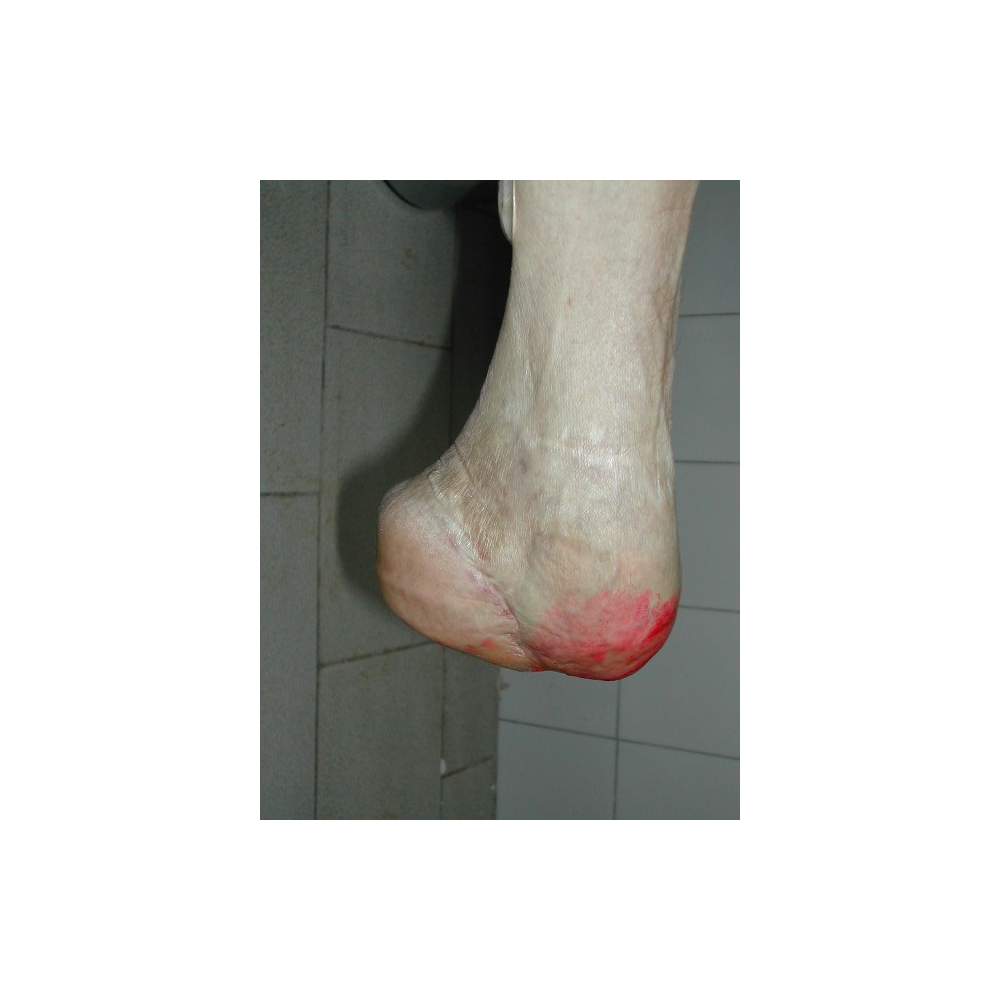
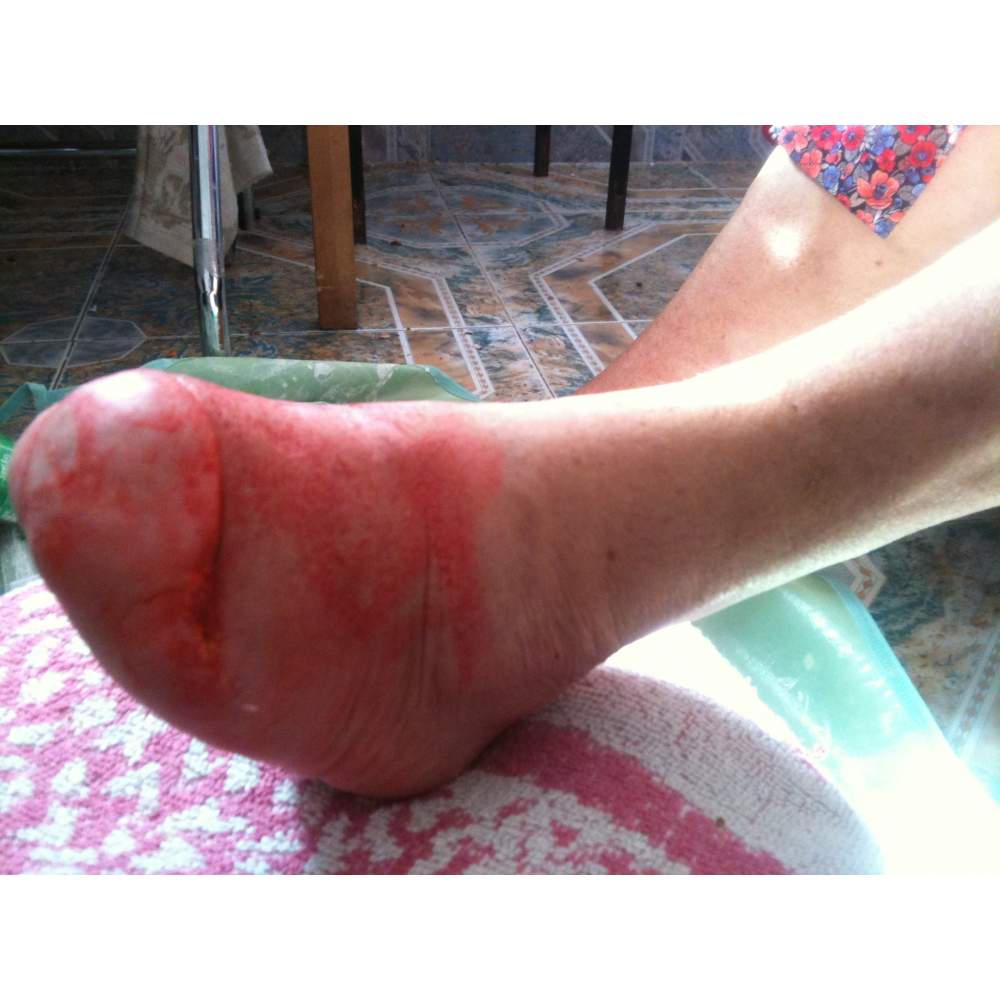
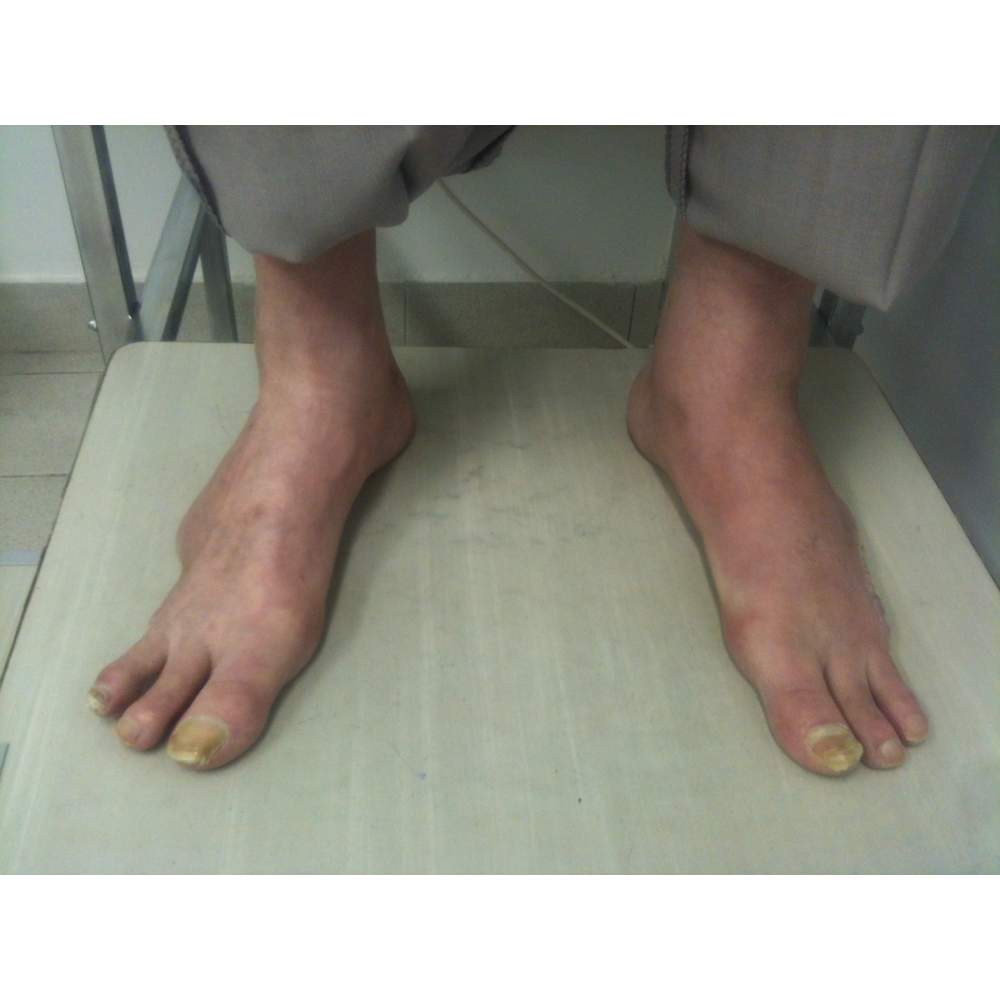
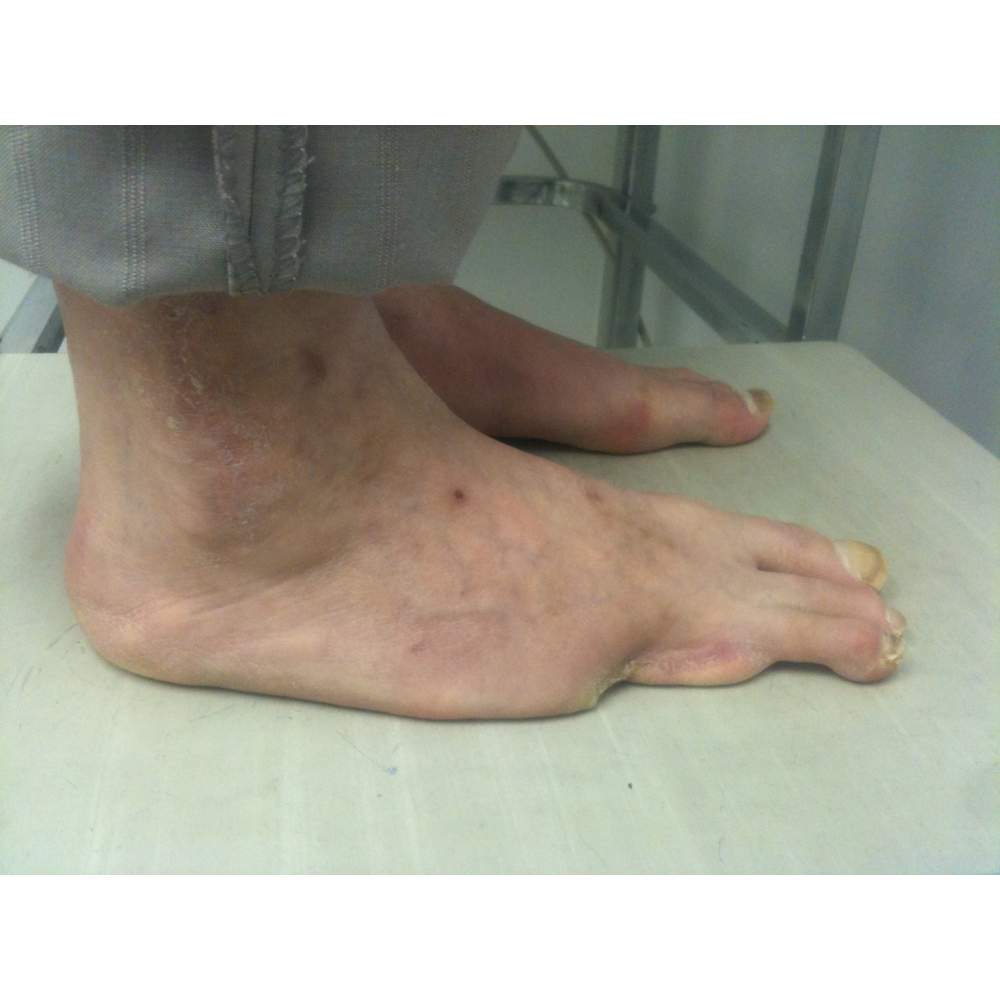
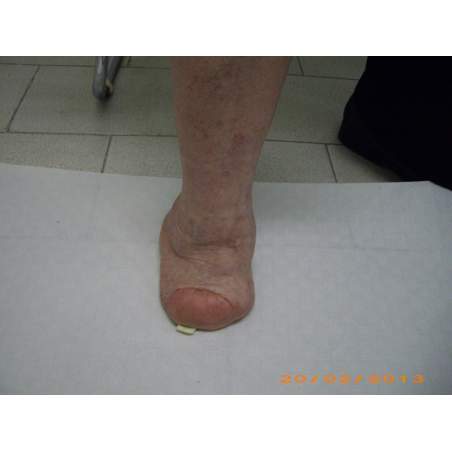
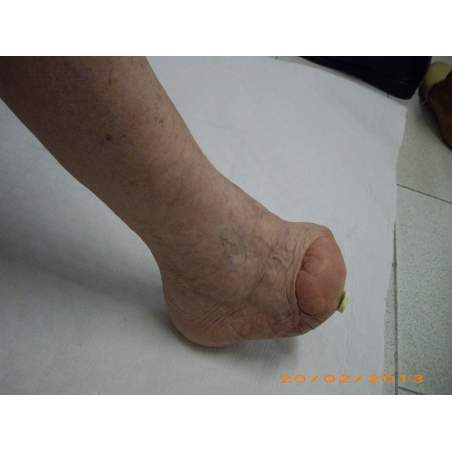
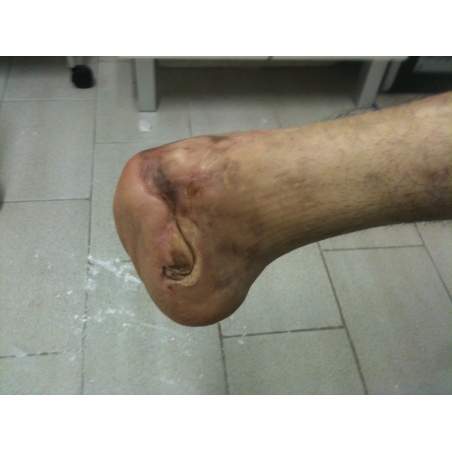
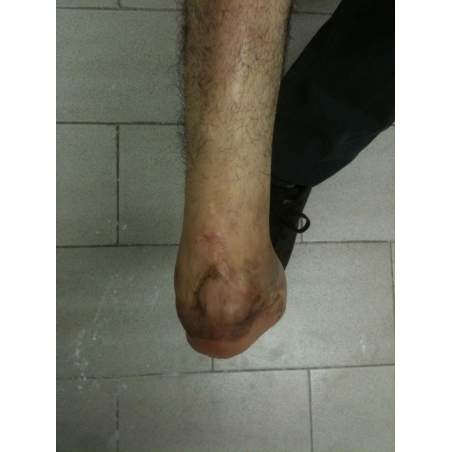
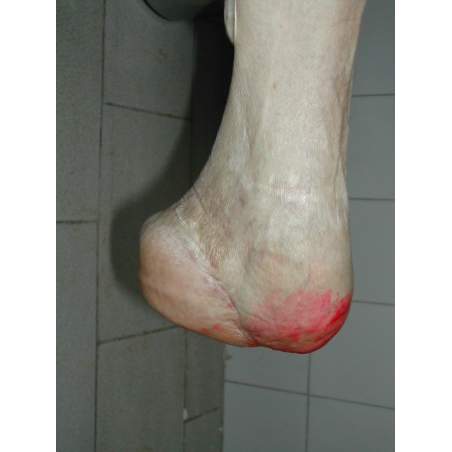
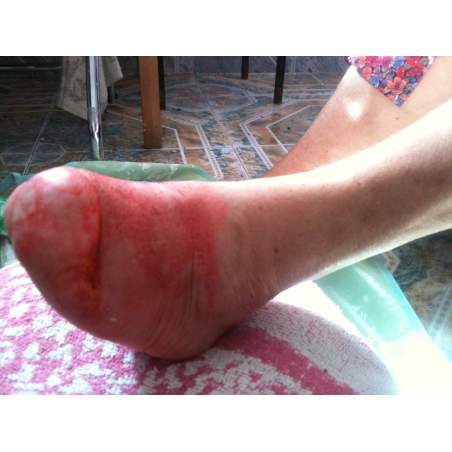
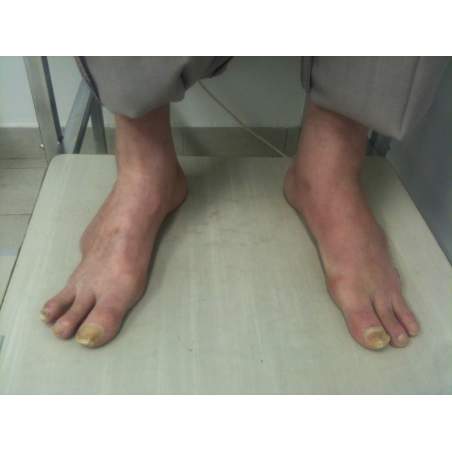
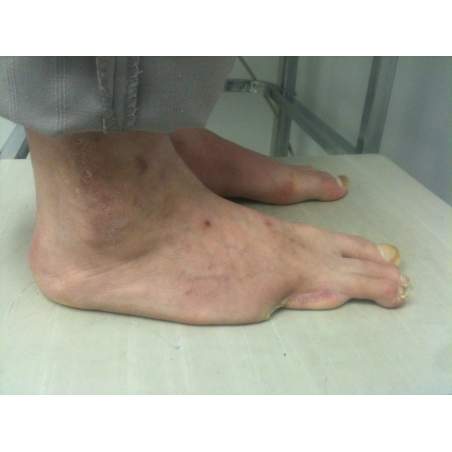
Many cases partial foot amputation
Several examples of partial foot amputation
Foot amputation
Is the removal of a leg, foot or toes. These body parts are called extremities. Amputations occur either by surgery, injury or trauma.
Why the Procedure Is Performed
Reasons for amputation of a lower limb are:
- Severe limb trauma caused by an accident.
- Poor blood flow to the limb.
- Infections that do not go away or become worse and can not be controlled or cured.
- Tumors of the lower extremity.
- Severe burns or severe frostbite.
- Wounds that do not heal.
Risks
Risks for any surgery are:
- Blood clots in the legs that may travel to the lungs
- Breathing problems
- Indented
Risks for this surgery are:
- A feeling that the limb is still there. This is called phantom sensation. Sometimes it can be painful. This is called phantom limb pain.
- The joint closest to the part amputated loses its range of motion, which makes it difIcil move. This is called joint contracture.
- Infection of the skin or bone.
- The amputation wound does not heal properly.
Before the procedure
When amputation is planned, you will be asked to take certain steps in order to prepare. Always tell your doctor or nurse:
- What medications you are taking, even drugs, supplements, or herbs you bought without a prescription.
- If you have been drinking a lot of alcohol.
During the days before the surgery, you may be asked to stop taking aspirin (aspirin), Ibuprofen (such as Advil or Motrin), warfarin (Coumadin), and any other drug that hinders blood clotting.
Ask your doctor which drugs you should still take on the day of surgery. If you smoke, stop.
If you have diabetes, follow your diet and take medication as usual until the day of surgery.
On the day of the surgery, most of the time you will be asked not to eat or drink anything for 8-12 hours before the procedure.
Take all medications as directed by your doctor with a small sip of water. If you have diabetes, follow the instructions given by the doctor.
Prepare your home prior to surgery:
- Plan what help you will need when you return from the hospital.
- MakeArrange for a family member, friend or neighbor help. If not, ask your doctor or nurse for help planning for someone to go home.
- Check the bathroom and the rest of the house is safe for you to move. For example, remove tripping hazards such as rugs.
- Verify that you can get in and out of your home safely.
After the procedure
The end of your leg (stump) have a dressing and bandage to remain on for 3 or more days. Will be painful for the first few days and you can take painkillers if needed.
You may have a tube that drains fluid from the wound, which will be removed after a few days.
Before leaving the hospital, you will begin to learn how to:
- Use a wheelchair or walker.
- Stretching the muscles to strengthen them.
- Strengthen your arms and legs.
- Start walking with a walking aid and parallel bars.
- Start moving around the bed and into the chair in her hospital room.
- Keeping joints moving.
- Sitting or lying in different positions to prevent joints from becoming stiff.
- Controlling swelling in the area around the amputation.
- Place appropriate weight on the stump. Le dirn how much weight to put on it. Possibly not allow putting weight on the leg until the stump has healed completely.
The fit of the prosthesis, artificial part to replace your limb, may occur when the wound mostly healed and the surrounding area is no longer sensitive to touch.
Prognosis
His recovery and ability to function after an amputation depend on many factors. Some of these are the reason for the amputation, if you have diabetes or poor blood flow, and age. Most people can still be active after amputation.
Alternative Names
Foot Amputation, Amputation of the leg; transmetatarsal Amputation, Amputation below the knee amputation below-knee amputation above the knee amputation above the knee, transfemoral amputation, Trans-tibial amputation